Flow Meter Straight Length Requirements are fundamental rules in flow measurement. These requirements ensure that flow meters, devices that measure the amount of liquid or gas that passes through them, work accurately. The installation of commonly used flow meters will require upstream and downstream straight pipe sections. Such as turbine flowmeter, electromagnetic flowmeter, vortex flowmeter, orifice flowmeter, etc.
Simply put, they ensure the fluid flows smoothly, minimizing disturbances that can skew readings. Adhering to these guidelines is crucial, as it guarantees precise results, allowing industries to operate efficiently and safely.
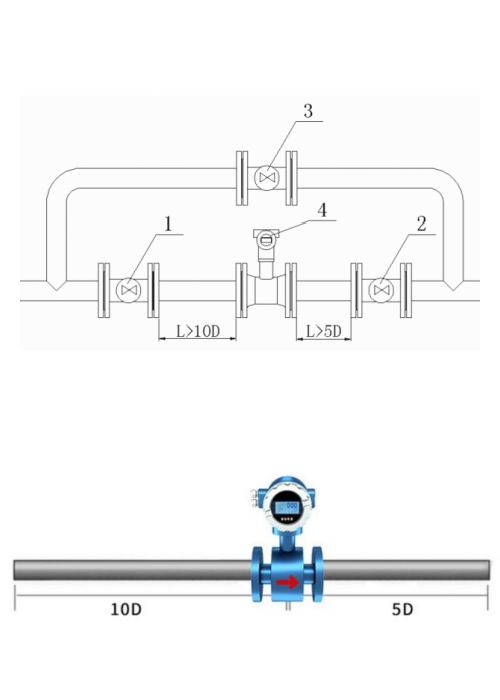
I’m not sure about you, but for me, my first question is, are there flow meters that are installed without straight pipe requirements?
The answer is yes. What I know so far are Gear flow meters (Oval gear flowmeter and circular gear flowmeter) and Coriolis mass flow meters. These two flowmeters do not require straight pipe sections during installation.
So, if your installation conditions are limited. Then you can consider these two flowmeters that do not require straight pipe sections.
Alternatively, if you know of other types of flow meters that do not require a straight pipe section during installation, please leave a comment.
Different Flow Meter Types and Their Straight Length Needs
| Flowmeter type | General requirements |
| Orifice plate: | The upstream shall not be less than 5 to 80 times the pipe diameter, and the downstream shall not be less than 2 to 8 times the pipe diameter; |
| Mass flowmeter: | No request; |
| Nozzle: | The upstream shall not be less than 5 to 80 times the pipe diameter, and the downstream shall not be less than 4 times the pipe diameter; |
| Venturi tube, elbow tube, wedge tube: | The upstream shall not be less than 5 to 30 times the pipe diameter, and the downstream shall not be less than 4 times the pipe diameter; |
| Equalizing tube: | The upstream shall not be less than 3 to 25 times the pipe diameter, and the downstream shall not be less than 2 to 4 times the pipe diameter; |
| Rotameter: | The upstream shall not be less than 0 to 5 times the pipe diameter, and there is no requirement for the downstream; |
| Target flow meter: | The upstream shall not be less than 5 times the pipe diameter, and the downstream shall not be less than 3 times the pipe diameter; |
| Turbine flowmeter: | The upstream shall not be less than 5 to 20 times the pipe diameter, and the downstream shall not be less than 3 to 10 times the pipe diameter; |
| Vortex flowmeter: | The upstream shall not be less than 10 to 40 times the pipe diameter, and the downstream shall not be less than 5 times the pipe diameter; |
| Electromagnetic Flowmeter: | The upstream shall not be less than 5 to 10 times the pipe diameter, and the downstream shall not be less than 0 to 5 times the pipe diameter; |
| Ultrasonic flow meter: | The upstream shall not be less than 10 to 50 times the pipe diameter, and the downstream shall not be less than 5 times the pipe diameter; |
| Positive displacement flow meter: | No request. |
| These requirements apply to our Sino-Inst brand flowmeters. It does not limit other brands of flowmeters. | |
More details about: Different Flow Meter Installation Rule of Thumb
Straight Run Requirements for Flow Meters
Certain flow meter technology types require that the flow profile within the piping system near the flow meter be linear , not turbulent , to eliminate flow meter malfunction or inaccuracy. Variables within the process system can cause turbulence.
Straight run requirements are expressed as a distance away from the flow meter, in a multiplication factor of the pipe diameter.
Requirements for the upstream value and the downstream value can be the same or they can be different, .
Read more about: what is upstream and downstream flow?
Why are Flow Meter Straight Length Requirements Necessary?
Straight pipe runs for flow meters aren’t just a recommendation; they’re a requirement for a vital reason. At the core, flow meters aim to measure fluid or gas flow accurately. However, the journey of these substances within pipes isn’t always a straight path. Turbulence, swirls, and chaotic flow patterns can develop, especially when the fluid encounters obstructions like bends, valves, and other instruments.
So, why do these flow disturbances pose a challenge? The crux of the matter is that turbulent flows make it tough for many flow meters to capture reliable readings. In scenarios where the flow becomes disorderly near the flow meters, the readings can be drastically off – sometimes deviating by as much as 50%!
Various elements in a piping system can cause these disturbances. Common culprits include pipe bends, control valves, T-joints, instrumentation installations, and even factors like pressure taps or reducers. All these elements can redirect the flow in unpredictable ways, hindering the meter’s ability to gauge accurately.
Therefore, to safeguard the integrity of flow measurements, ensuring a smooth, undisturbed flow profile through straight pipe runs is paramount. It’s not just about adhering to guidelines; it’s about ensuring that industries get precise data to make informed decisions.
FAQ
Choosing a Flow Meter for Your Application
More Flow Measurement Solutions
What is an Ammonia Flow Meter and How to Choose?
Industrial Online Dew Point Meters | Sino-Inst
Industrial Slurry Density Measurement-Featured Slurry Density Meters
Density 101: What Is the Unit of Measurement for Density
Industrial Applications of Various Density Meters
What Is a Coriolis Mass Flowmeter and How Does It Work?
Understanding the nuances of Flow Meter Straight Length Requirements is essential for anyone looking to ensure accurate and consistent flow measurements. While the need for straight runs might seem technical, it’s fundamentally about achieving the undisturbed flow profile necessary for optimal meter performance.
However, flow measurement is just a facet of the intricate world of industrial instrumentation. At Sino-Inst, we also offer expertise in density measurement, gas analysis, torque sensors, liquid level measurement, and temperature measurement. Each domain, while unique, is bound by our commitment to precision, quality, and innovation.
With vast experience in the field, Sino-Inst stands as a trusted manufacturer and supplier, dedicated to meeting diverse industrial needs. Ready to explore a world of high-quality instrumentation? Contact Sino-Inst today and let our team guide you to the perfect solution for your measurement needs.
Request a Quote
Wu Peng, born in 1980, is a highly respected and accomplished male engineer with extensive experience in the field of automation. With over 20 years of industry experience, Wu has made significant contributions to both academia and engineering projects.
Throughout his career, Wu Peng has participated in numerous national and international engineering projects. Some of his most notable projects include the development of an intelligent control system for oil refineries, the design of a cutting-edge distributed control system for petrochemical plants, and the optimization of control algorithms for natural gas pipelines.