Gauge Pressure Transmitter/Transducer for process, oil and gas industry. With HART®-Communication and SIL2 (optionally).

Gauge Pressure Transmitter / transducer (GP) is a pressure transmitter for Gauge pressure measurement. Gauge pressure transmitter can measure the pressure of liquid, gas or steam. And convert it into 4 ~ 20mA DC signal output. The GP pressure transmitter can communicate with the HART Communicator, through which it can be set and monitored. Gauge pressure refers to pipeline pressure. “Gauge pressure” starts from atmospheric. Gauge Pressure plus atmospheric is the absolute pressure.
Sino-Inst offers a variety of Gauge pressure transmitters for industrial pressure measurement. If you have any questions, please contact our sales engineers.
Features of Gauge Pressure Transmitter

- Nominal pressure: from 0 … 400 mbar up to 0 … 600 bar
- Output signals : 2-wire: 4 … 20 mA ; others on request
- Special Characteristics:
- turn-down 1:10
- two chamber aluminum die-cast case or stainless field housing
- internal or flush welded diaphragm
- HART®-communication
- IS-version: Ex ia = intrinsically safe for gases and dusts
- accuracy: 0,1 % FSO
- Optional versions
- IS-version: Ex d = flameproof enclosure
- SIL2 – version according to IEC 61508 / IEC 61511
- integrated display and operating module
- special materials as Hastelloy® and Tantalum
- cooling element for media temperatures up to 300 °C
- Read more about: Common Units Of Pressure
Specifications of Gauge Pressure Transmitter
| Use object: | Liquid, gas or steam |
| Measuring range | 0-3.5~35kPa 0-10~100kPa 0-35~350kPa 0-0.1~1.0MPa 0-0.35~3.5MPa 0-1.0~10MPa 0-2.1~21MPa 0- 4.1~41Mpa 0- 6.0~60MPa |
| Output signal: | 4-20mAdc. Output, superimposed HART protocol digital signal (two-wire system) |
| Power source: | External power supply 24V dc. Power supply range 12V ~ 45V |
| Installation in dangerous places | Flameproof ExdIIBT5Gb; (explosion-proof certificate no. :CE16.1163) Intrinsically safe ExiaIICT4/T5/T6Ga; (explosion-proof certificate no. : CE15.2354X) |
| Accuracy: | ±0.1%, ±0.075% |
| Stability: | ±0.2%/12 months of the maximum range |
| Temperature effect: | Including zero and range for maximum temperature error of ±0.2% / 20 ℃ |
| Power supply impact: | Less than 0.005% / V of the output range. |
| Vibration effect: | In any axial direction, the frequency is 200Hz, and the error is ±0.05% / g of the maximum range. |
| Electronic circuit board work in: | – 40 ~ 85 ℃; |
| Sensitive components work in : | – 40 ~ 85 ℃; |
| Storage temperature : | – 40 ~ 85 ℃; |
| With digital display: | – 25 ~ 75 ℃ (run); – 40 ~ 85 ℃ (no damage); |
| Relative humidity: | 0 ~ 95% |
| Overpressure limit: | 2~5 times the maximum range of pressure transmitter is not damaged. |
| Volume change: | Less than 0.16cm3 |
| Damping: | The time constant is adjustable from 0.1 to 32.0s. |
| Startup time: | 3s, no preheating required. |
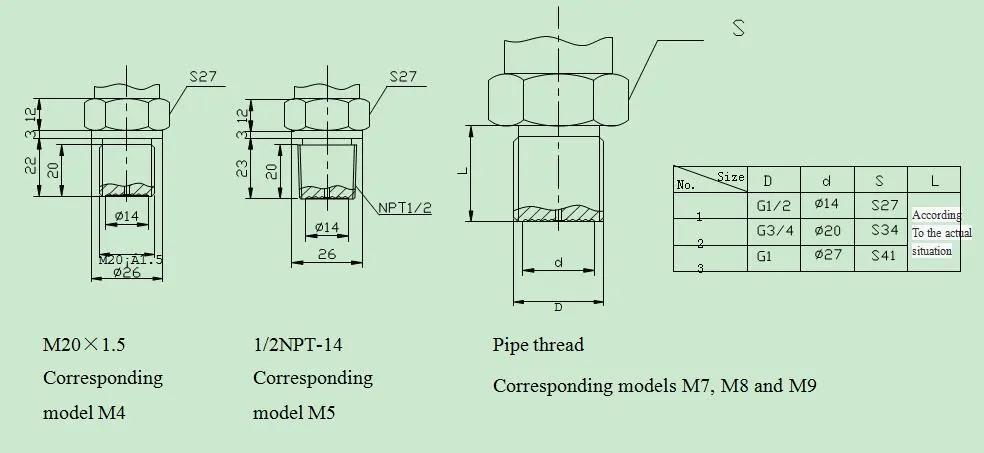
Extended reading: How to calibrate HART pressure transmitters
Common Industrial Applications of Gauge Pressure Transmitter
- Mechanical and plant engineering
- Chemical industry
- Medical technology
- Food and beverage
- Oil and gas industry
- Packaging and paper industry
- Pharmaceutical industry
You may like: Explosion Proof Pressure Transmitter for Hazardous locations
What is a Gauge Pressure Transmitter?
Gauge Pressure Transmitter is one of the common industrial process pressure transmitters. Mainly used to measure the pressure of liquid, gas and other gauges. HS code: 9026201090.
A gauge pressure (GP) transmitter compares the process pressure with the local ambient air pressure. The gauge pressure transmitter has a port for real-time sampling of ambient air pressure.
High-precision gauge pressure transmitters may be affected by local environmental pressure fluctuations. Measurements above ambient pressure are expressed as positive numbers. A negative number indicates a measured value below ambient pressure.
The gauge pressure measurement value is indicated by the letter “g” after the unit of measurement (ie, inH 2 O (g) or psig).
Read more about: What is industrial pressure transmitter?
Gauge pressure transmitter working principle
SMT3151 TGP-Gauge Pressure Transmitter / Transducer is a diffusion silicon pressure transmitter. The working principle of the diffused silicon pressure sensor is based on the piezoresistive effect. Using the principle of piezoresistive effect, the pressure of the measured medium directly acts on the diaphragm of the sensor (stainless steel or ceramic). Make the diaphragm produce a slight displacement proportional to the pressure of the medium. To change the resistance value of the sensor. Use electronic circuits to detect this change. And convert and output a standard measurement signal corresponding to this pressure.
More about : Pressure transmitter Working Principle.
Difference between absolute, gauge and differential pressure
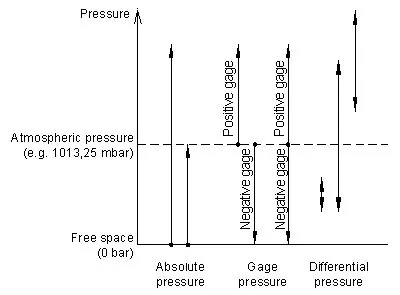
Absolute pressure
Absolute pressure is referred to as the vacuum of free space (zero pressure). In practice, absolute piezoresistive pressure sensors, measure the pressure relative to a high vacuum reference, sealed behind its sensing diaphragm. The vacuum has to be negligible compared to the pressure to be measured. Sino-Instrument’s absolute pressure sensors, offer ranges from 1 bar or even 700 mbar as well as barometric pressure ranges.
Gage pressure
Gage pressure is measured relative to the ambient atmospheric. The average atmospheric at sea level is 1013.25 mbar. Changes of the atmospheric, due to weather conditions, or altitude influences the output of a gauge pressure sensor.
A gauge pressure higher than ambient pressure is referred to as positive pressure. If the measured pressure is below atmospheric, it is called negative or vacuum gage pressure. In general, a vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter.
According to its quality vacuum is divided into different ranges such as an e.g. low, high and ultra high vacuum.
Differential pressure
Differential pressure is the difference between any two process pressures p1 and p2. Differential pressure sensors must offer two separate pressure ports, with a tube or thread. Sino-Instrument’s amplified pressure sensors, are able to measure positive and negative pressure differences. i.e. p1>p2 and p1<p2.
These sensors are called bidirectional differential pressure sensors, with ranges of e.g. -1…+1.0 bar or -2.5…+2.5 mbar. In contrast, unidirectional differential pressure sensor only operate in the positive range (p1>p2). E.g. from 0…1.0 bar or 0…2.5 mbar. And the higher has to be applied to the pressure port defined as “high pressure”.
Gauge Pressure VS Absolute Pressure
- Gage pressure refers to pipeline pressure. It refers to the pressure measured with pressure gauges, vacuum gauges, U-shaped tubes and other instruments, also called relative pressure). “Gage pressure” starts from atmospheric pressure.
- The pressure directly acting on the surface of the container or object is called “absolute pressure”. The absolute pressure value starts with absolute vacuum.
Absolute pressure actually refers to the gauge pressure plus the local atmospheric pressure (generally a standard atmospheric pressure can be 101.3Kpa).
Absolute pressure = gauge pressure + one atmosphere
If the unit is MPa, absolute pressure = gauge pressure + 0.1MPa
Read more about: Absolute Pressure Vs Gauge Pressure Measuring Instruments
More Featured Pressure Transmitters:
Q & A
What is the difference between pressure gauge and pressure transmitter?
The difference between pressure transmitter and pressure gauge are:
1. The accuracy of standard instruments required for pressure transmitter calibration is much higher than that required for pressure gauges.
2. The pressure gauge only needs to verify a pair of input and output relationships. The pressure transmitter may need to verify the relationship between the input and the communication data.
3. The calibration of the pressure gauge must have corresponding measurement qualifications. Pressure transmitters are generally not required except for production plants and new construction.
4. The pressure gauge has poor accuracy and no output. Do not use a hand-operated device. Generally check 5 points, the difference between the back and forth is different. The intelligent pressure transmitter generally only needs to check the zero point and full range.
5. The output of the pressure gauge is scale indication, and its own display ability. The pressure transmitter is a current output, which must be connected to an ammeter of the corresponding accuracy level for display.
What is the working principle of pressure transmitter?
Pressure transmitter manufacturers use different terms for pressure measurement products of different designs, such as pressure sensor, pressure transmitter, pressure converter, etc.
In Sino-Inst, “pressure transmitter” is often used to describe pressure sensors equipped with standard electrical and mechanical interfaces and standard signal outputs.
The working principle of the pressure transmitter is as follows:
The pressure of the medium to be measured is transmitted through the standard process connection, and then affects the internal pressure sensor element. Internal electronic components convert the original transmitter signal into filtered, amplified, temperature compensated and standardized signals, such as 4 … 20 mA signals. The output signal is sent to the next unit for signal processing through standardized connectors or cables.
What is a strain gauge pressure transducer?
Strain gauge pressure sensors work based on the principle of resistance strain effect. There are two types of resistance strain gauges: metal strain gauges (metal wires or metal foils) and semiconductor strain gauges. The measured pressure causes the strain gauge to strain. When the strain gauge produces compressive strain, its resistance decreases. When the strain gauge produces tensile strain, its resistance increases. The change of the resistance value of the strain gauge, and then obtain the corresponding millivolt level potential output through the bridge circuit, and display the measured pressure with a millivoltmeter or other recording instruments, thereby forming a strain gauge pressure gauge.
What is pressure transducer used for?
In general, the pressure transmitter is mainly used to measure the pressure and liquid level of the medium. The pressure transmitter is an indispensable key component in the fluid industry. The pressure transmitter is mainly used in the following fields:
1. Petroleum, petrochemical, chemical industry, matching with throttling devices, providing accurate flow measurement and control. It can measure the pressure and liquid level of pipelines and storage tanks.
2. Electric power, city gas, and other company businesses that require high-stability and high-precision measurement.
3. Pulp and paper making are used in places requiring chemical resistance and corrosion resistance.
4. Steel, non-ferrous metals, ceramics, used in furnace pressure measurement and other places that require high stability and high precision measurement, and used in places where stable measurement is required under strict control (temperature, humidity, etc.).
5. Machinery and shipbuilding are used to strictly control places requiring stable measurement under high precision conditions.
How does a 3 wire pressure transducer work?
The three wires of a 3-wire pressure sensor are generally red, black, and yellow, which are power supply positive, power supply negative, and signal lines. The power supply is positively connected to the positive pole of the DC power supply, the power supply is negatively connected to the negative pole of the DC power supply, and the signal line is connected to the signal input port of the device.
The so-called three-wire system is to use a wire for the positive end of the power supply, a wire for the positive end of the signal output, and a common wire for the negative end of the power supply and the negative end of the signal. The power supply is mostly 24v.dc, the output signal is 4-20ma.dc, the load resistance is 250ω or 0-10ma.dc, and the load resistance is 0-1.5kω; some also have ma and mv signals, but the load resistance or input The value of resistance varies with the output circuit.
The title of several-wire system comes after the birth of two-wire transmitter. This is the result of the widespread application of electronic amplifiers in meters. The essence of amplification is an energy conversion process, which is inseparable from power supply. Therefore, the first to appear is a four-wire transmitter; that is, two wires are responsible for the power supply, and the other two wires are responsible for outputting the amplified signal (such as voltage, current, etc.).

Wu Peng, born in 1980, is a highly respected and accomplished male engineer with extensive experience in the field of automation. With over 20 years of industry experience, Wu has made significant contributions to both academia and engineering projects.
Throughout his career, Wu Peng has participated in numerous national and international engineering projects. Some of his most notable projects include the development of an intelligent control system for oil refineries, the design of a cutting-edge distributed control system for petrochemical plants, and the optimization of control algorithms for natural gas pipelines.



