
DP transmitters are Differential Pressure Transmitters. DP transmitter measures the pressure difference between the gas or liquid at both ends of the transmitter. Output 4~20mA, 0~5V. Used for liquid level, density and pressure of liquid, gas and steam.

DP transmitters are different from pressure transmitters as they have 2 pressure interfaces. With flanges, capillaries, valve, brackets, throttle devices. Differential pressure transmitters are used to measure the level, density, and flow of liquids, gases, and vapors. Then convert it into 4–20mADC current signal output.
Sino-Inst offers a variety of DP transmitters for industrial pressure measurement. If you have any questions, please contact our sales engineers.
Featured DP transmitters

Piezoresistive Differential Pressure Transmitter utilizes the piezoresistive effect of semiconductor silicon materials. Realize accurate measurement of differential pressure.

Smart Differential Pressure Transmitter measures industrial differential pressure. Can Works with diaphragm seals, capillary, HART. Outputs standard signals (such as 4 ~ 20mA, 0 ~ 5V).

Flange Mounted Differential Pressure Transmitter is also called single flange DP level transmitter. For liquid, gas or vapor pressure measurement.

Extended Diaphragm Seal DP Transmitter is a level transmitter direct mounted on pipe or tank. The isolation diaphragm is in direct contact with the liquid medium.

Remote Seal DP Transmitter is often used as a tank level transmitter. The smart pressure transmitter is connected with a stainless steel flange by capillary. The pressure is sensed by a remote transmission device installed on a pipe or container.

Differential pressure (DP) level transmitter is a perfect solution for tank level measurement. Flanges, seal diaphragms, capillaries, and DP transmitter are often used to measure liquid levels.

Quickly measure the positive, negative or DP of air or non-corrosive gas. Sino-Inst supplies Differential Pressure Gauges made in China. DWYER 2000 Differential Pressure Gauges, Magnehelic differential pressure gauges are also available.
Differential Pressure Transmitters Technology Guide
What is a Differential Pressure Transmitter?
Differential pressure (DP) transmitter, also known as differential pressure transducer. The most common and useful industrial pressure measuring instrument is DP transmitter.
A differential pressure transmitter measures the difference between two pressures. The differential pressure transmitter converts the pressure measurement to a proportional 4-20 mA or 1-5 Vdc output signal. Used as input for controllers, recorders, indicators or similar devices.
The DP transmitter will sense the pressure difference between the two ports according to the calibrated pressure range and generate an output signal. Industrial differential pressure transmitters are made of two housings.
The pressure sensing element is located in the lower half, and the electronic element is located in the upper half. It will have two pressure ports labeled “High” and “Low”. The high-pressure port is always in a high-pressure state. It is not mandatory that the low-voltage port is always in a low-voltage state. This mark is related to the effect of the port on the output signal.
DP readings can be negative or positive, depending on the low-end or high-end. If the low-pressure side is open to the atmosphere, the DP transmitter can be used as a gauge pressure transmitter.
Through its 4… 20 mA, HART®, PROFIBUS®PA or FOUNDATION Fieldbus ™ output signal, combined with intrinsic safety or fire protection.
Differential pressure transmitters are suitable for applications that require these functions. All electronic devices with explosion-proof transmitters are safe. Therefore, the instrument can be adjusted in the EX area when the instrument is energized.
Sino-Instrument’s DP transmitters can work with AMS TREX device.
Features of DP transmitters
- Widely used
DP transmitters are the basic measurement equipment in industrial measurement. Under different measurement environments, pressure, liquid level, flow, and density can be measured. - Suitable for harsh working conditions
High temperature, explosion-proof and anti-corrosion can use DP transmitters. By adding flanges, capillaries, brackets, etc., remote measurement can be performed.
You may like: Diaphragm pressure gauge
Differential Pressure Transmitter Applications
Differential pressure transmitter for measuring liquid level
Differential pressure liquid level transmitter has single flange and double flange.
- The single flange is used to measure the liquid level of the open tank.
Differential pressure range calculation method: need to measure the liquid level height (unit: m) × gravity acceleration (9.8) × measured medium density (unit: g / cm3, when the density of water is calculated as 1, the unit is g / cm3) Range (unit: KPa).
The type selection must know the measuring medium, measuring range, medium temperature, process connection flange size and pressure rating and flange standard. - Double flange is used to measure the liquid level of the closed tank.
Closed tank level measurement using dp transmitter, Differential pressure range calculation method: need to measure liquid level height (unit: meter) × gravity acceleration (9.8) × (measured medium density-capillary filling liquid density) (unit: g / cm3) = differential pressure range (unit: KPa ).
The type selection must know the measurement medium, measuring range, medium temperature, pressure, capillary length, process connection flange size and pressure rating, and flange standard.
Read more about: Use Differential Pressure Transmitter to Measure Liquid Level
Differential pressure transmitter to measure flow
- From the working principle of the differential pressure flow transmitter: the differential pressure flow transmitter can calculate the pipeline flow by measuring the pressure difference between the two ends of the throttle device. The differential pressure transmitter measures the flow rate, which is mainly connected to the two holes perpendicular to the flow axis of the throttling device through the hose. What they sense is the static pressure difference between the two sections. By the principle of energy conservation, the static pressure difference between the two sections is approximately equal to the dynamic pressure difference between the two sections. Because the dynamic pressure is proportional to the square of the flow velocity, the flow velocity is inversely proportional to the square of the diameter of the over-flow section. Therefore, by measuring the static pressure difference between the two sections, the flow velocity and flow rate of the section can be obtained.
- Application of differential pressure flow transmitter in steam metering system
The differential pressure transmitter measures the flow rate and needs to be used in conjunction with the orifice flowmeter and flow totalizer. Indispensable. There are two pressure pipes on the orifice flowmeter, and these two pressure pipes are connected to the high and low pressure chambers of the differential pressure transmitter. The measured flow is that water is flowing, so there will be direction and flow size. The differential pressure transmitter measures the differential pressure at two points. Output analog signal to flow totalizer to accumulate flow.
Differential pressure transmitter for density measurement
For differential pressure transmitters: differential pressure △ P = density hundred ρ × liquid level height h × gravity acceleration g
When measuring the liquid level, ρ and g are constants, and △ P is a function of h;
If h and g are constants, ΔP is a function of ρ. You can measure the density;
The specific method is to connect the positive and negative pressure of the transmitter to the liquid level (h is a fixed value), and the measured differential pressure is related to the density.
Note that in order to keep the liquid density in the pressure tube unchanged (otherwise it will affect the measurement results), it is usually necessary to fill the pressure tube with isolation liquid.
Differential pressure transmitter working principle
What is pressure?
Physical pressure refers to the force that occurs on the contact surface of two objects. Or the vertical force of gas on the surface of solid and liquid. Or the vertical force of the liquid on the solid surface.
The pressure (or differential pressure) measured by the transmitter is the pressure.
Force refers to the force that occurs on the contact surface of two objects. Or the vertical force of gas on the surface of solid and liquid. Or the vertical force of the liquid on the solid surface.
Pressure refers to the ratio of the pressure on the object to the area under pressure. Or it is the force per unit area. Pressure is used to compare the effects of pressure. The greater the pressure, the more obvious the effect of pressure.
Traditionally, in mechanics and most engineering disciplines, the term “force” is synonymous with pressure in physics. In fact, to discuss force or pressure, just look at its unit. If stress is a Newton, it is force. If one square meter bears one Newton, it means pressure. (1N / ㎡ = 1Pa)
Most Common Types of Pressure
We use three common types in the industry.
- The first is “gauge pressure”. Measured with reference to atmospheric pressure (typically 14.7 PSI). When above atmospheric pressure, you will display a “positive” pressure; when below atmospheric pressure, you will display a “negative” pressure.
- The next is “absolute pressure“. In short, this is the pressure relative to an absolute vacuum measurement. The absolute pressure of the full vacuum is zero PSIa and it increases from there. This type of sensor can be used if it is necessary to read pressures below atmospheric pressure.
- The last type that is usually monitored in the industry is “pressure differential”. It sounds like this, the difference between two pressures, a measured pressure and a reference pressure.
Extended Reading: Smart pressure transmitter
How does a differential pressure transmitter work?
- Process pressure isolates the diaphragm through two or one sides.
- The filling fluid acts on the tensioned measuring diaphragm in the delta element (ie the sensitive element).
- The measuring diaphragm and the capacitor plates on both sides of the insulator form a capacitor.
- The diaphragm is in the middle position when there is no pressure in or the pressure on both sides is equal. The capacitance of the two capacitors is equal.
- When the pressure on both sides is inconsistent, the measurement diaphragm will be displaced. The displacement is proportional to the pressure difference. This displacement is converted into a differential capacitor formed on the capacitor plate.
- The electronic circuit converts the differential capacitor into a two-wire current signal of 4-20mADC.
- The working principle of the pressure transmitter and the absolute pressure transmitter is the same as the differential pressure transmitter. The difference is that the pressure in the low-pressure chamber is atmospheric pressure or vacuum.

The Components of a Differential Pressure Transmitter
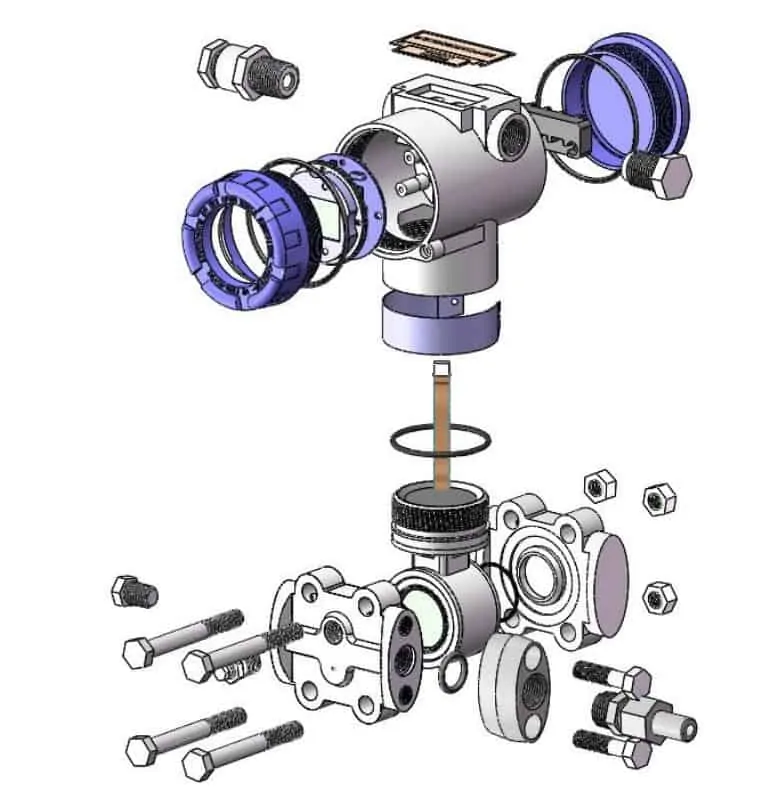
The differential pressure transmitter is mainly composed of a detection part and a signal conversion and amplification processing part.
1) Direct pressure sensing element (located in the lower housing).
Most industrial DP transmitters are equipped with diaphragms as pressure sensing elements. The diaphragm is a mechanical device. It is placed between two pressure inlets. The diaphragm will deflect due to the applied pressure. This deflection is converted into an electrical signal. This is usually done by sensors. Commonly used sensors are (a) strain gauges (b) differential capacitance (c) vibrating wire. The sensor output is proportional to the applied pressure.
2) Electronic unit: The electrical signal generated by the sensor in the lower chamber is only in the range of millivolts. The signal will be amplified to the 0-5V or 0-10V range, or converted to 4-20mA to continue transmission to the remote instrument. The upper housing is the transmitter part of the DP transmitter, which houses the electronic unit. DC output current is generated, which is proportional to the pressure range of the differential pressure transmitter. The lower limit is 4mA and the upper limit is 20mA. The controlled current output is not affected by load impedance changes and power supply voltage fluctuations. The 4-20mA output is superimposed with the digital communication of BRAIN or HART protocol.
Differential pressure transmitter installation
Where to install differential pressure transmitter
Selection of installation location of differential pressure transmitter:
- Corrosive or overheated media should not be in contact with the differential pressure transmitter.
- Prevent the slag from settling in the pressure tube.
- The hydraulic heads in the two pressure pipes should be balanced.
- The impulse tube should be as short as possible.
- The impulse tube should be installed in a place where the temperature gradient and temperature fluctuation are small.
- Measure the liquid flow: The pressure port should be opened on the side of the process pipe to avoid sedimentation. The differential pressure transmitter should be installed on the side or below the pressure tap to allow gas to escape into the process piping.
- Measurement of gas flow: The pressure tap should be opened on the top or side of the process pipe, and the differential pressure transmitter should be installed below the pressure tap to allow liquid to drain into the process pipe.
- Measure the steam flow: the pressure port should be opened at the top or side of the process pipe, and the transmitter should be installed below the pressure port, so that the condensate flows into the pressure pipe.
- When using a transmitter with an exhaust / drain valve on the side, the pressure port should be opened on the side of the process pipe. When the working medium is liquid, the exhaust / drain valve is on the top to remove gas. When the working medium is gas, the valve should be on the bottom to exclude liquid accumulation. Turning the flange 180 ° can change the exhaust / drain valve Up and down position.
Read more about: Installation method of differential pressure transmitter:

How do you install a differential pressure transmitter?
Follow the steps below to introduce process pressure into the impulse tube and transmitter:
Total Time:
Open the high-pressure and low-pressure side pressure-increasing valves to introduce process fluid into the pressure measuring part.
Slowly open the high-pressure shut-off valve and introduce the process liquid into the pressure measurement section.
Close the high-pressure shut-off valve.
Slowly open the low pressure shut-off valve to fully fill the pressure measurement part with process fluid.
Close the low pressure shut-off valve.
Slowly open the high-pressure shut-off valve. At this time, the pressure on the high and low sides of the transmitter is equal.
Confirm that there is no leakage of the pressure guiding tube, three-resistance valve, transmitter and other components.
Differential pressure transmitter calibration
How do you calibrate a differential pressure transmitter?
Calibration procedure steps:
- Set the differential pressure transmitter, HART communicator, power supply, manual pump and multimeter as shown below (see the calibration setup diagram below).
- Make sure the equalization valve manifold is closed.
- Apply a pressure equal to the lower range pressure to the transmitter (usually corresponding to 4 mA in the transmitter output). For example, we have a calibration range of 0 to 100 mBar, and then the low range pressure is 0, or we have -2 psig to 5 psig and then we have a lower range pressure equal to -2 psig.
- Read the pressure in the transmitter LCD (or HART communicator). Adjust (if any) through the HART communicator so that the transmitter output (on the LCD) is the same as the applied pressure.
- Use a multimeter to read the mA output of the transmitter. Adjust (if any) through the HART communicator so that the output of the transmitter (multimeter) is 4 mA.
- Apply pressure equal to the upper limit pressure to the transmitter (usually corresponding to 20 mA in the transmitter output).
- Read the pressure in the transmitter LCD (or HART communicator). Adjust (if any) through the HART communicator so that the transmitter output (on the LCD) is the same as the applied pressure.
- Use a multimeter to read the mA output of the transmitter. Make adjustments (if any) through the HART communicator so that the output of the transmitter (multimeter) is 20 mA.
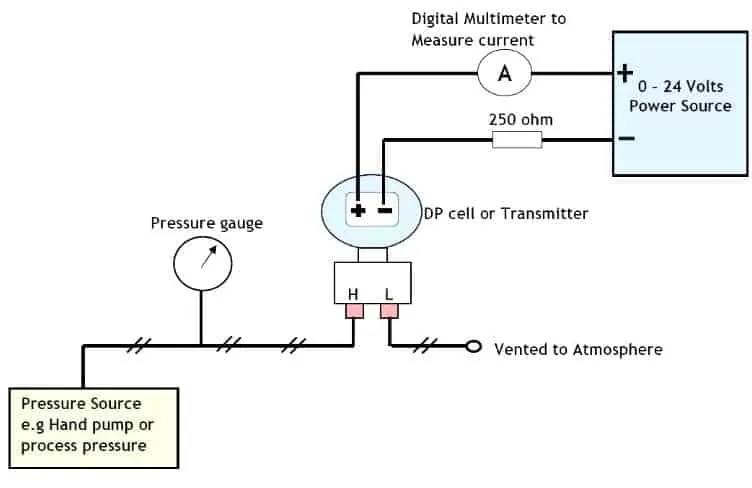
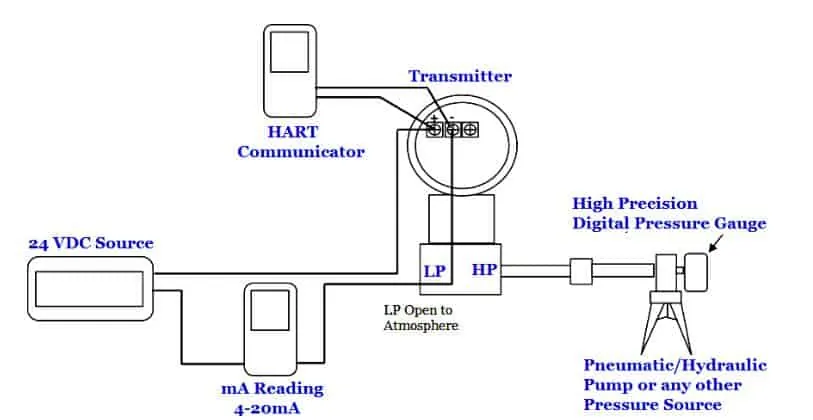
Read more about:
differential pressure transmitter price
How much does a differential pressure transmitter cost? And what factors influence that price?
The cost of a differential pressure transmitter can vary widely, depending on several factors. You can expect to pay anywhere from a few hundred to several thousand dollars for a transmitter.
However, it’s essential to understand that the price tag isn’t just about the device itself. It’s about the accuracy, reliability, and long-term performance it brings to your operation.
Factors Influencing Differential Pressure Transmitter Price
Let’s break down the factors that influence the price of a differential pressure transmitter into a simple list:
- Type of Medium: The nature of the medium being measured, such as its corrosiveness, can affect the price. If the medium is corrosive, the transmitter needs to be made of materials resistant to corrosion, which may increase the cost.
- Pressure Range: Transmitters designed to measure a broader range of pressures tend to cost more due to the complexity and flexibility of their design.
- Temperature Range: Similarly, transmitters that can accurately measure pressure at extreme temperatures can be more expensive. These devices must be designed to withstand and operate effectively in such conditions.
- Accuracy Requirements: The more precise the measurement required, the more expensive the transmitter.
- Installation Size: The size of the transmitter can impact the cost. The cost of threaded installation and flange installation is obviously different.
- Signal Output: Transmitters that offer various types of signal outputs (e.g., 4-20 mA, HART, Fieldbus) can be more costly due to their versatility.
- Local Display: Transmitters with built-in local displays for easy reading and monitoring can be more expensive than those without.
Considering these factors can help you make a more informed decision when purchasing a differential pressure transmitter.
Remember, the most cost-effective choice may not always be the cheapest. But the one that best suits your specific needs and offers the best long-term value.
low cost differential pressure sensor
The compact differential pressure transmitter is a low cost differential pressure sensor. The stainless steel shell, strict production process, and small installation volume ensure the excellent performance of this series of products. And it is small in size and easy to install. It is the general choice for small differential pressure, flow field, flow velocity and flow measurement.
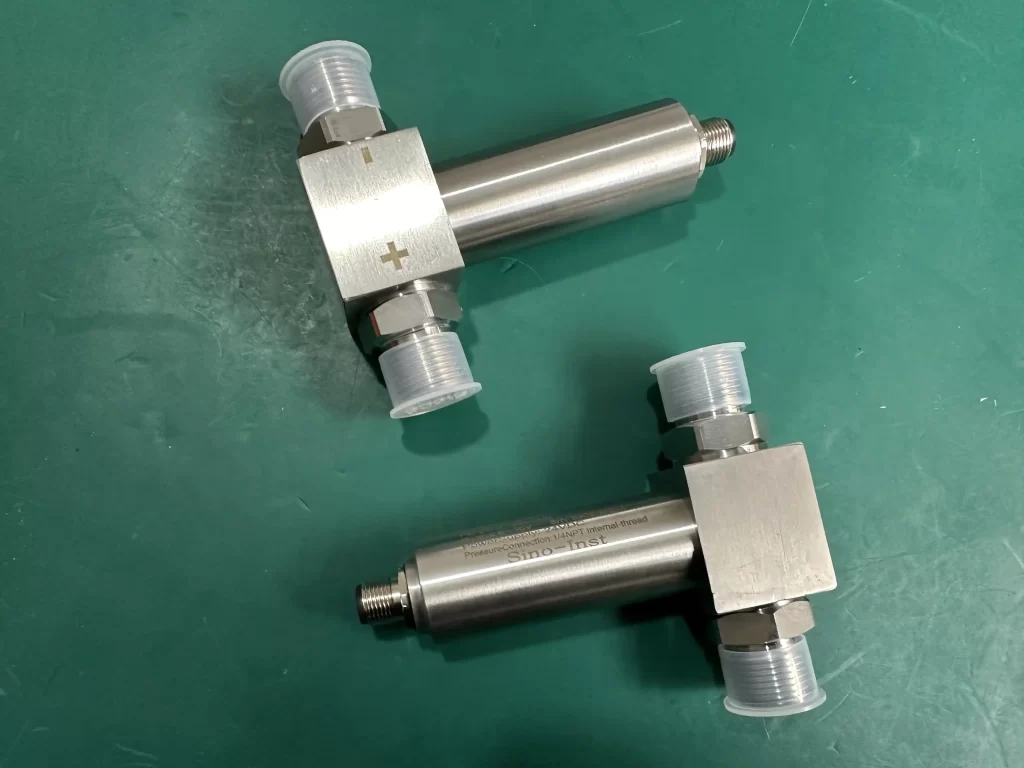

Features of compact differential pressure transmitter
- High performance price ratio
- All stainless steel structure design, small size and light weight, easy to install
- Stable and reliable performance
- Differential pressure range: 0~10kPa…2MPa
- Static pressure resistance up to 20MPa
Low cost differential pressure sensor product Applications
- Industrial process control
- Flow measurement
- Medical instrument
- Aerodynamic measurements
- Hydraulic and pneumatic equipment
Tools for converting and calculating pressure values. Help you choose suitable pressure sensors and transmitters!
If you would like any more information about our differential pressure sensors,
please send your inquiry now.






FAQ
You may like:
Top Digital Pressure Transducers with Display
Custom Case: Pressure Transducer Connector with 6 Pin Bendix Connector
Why Shielded Twisted Pair Cables for Industrial Instrumentation
Wetted Materials of Pressure Senors – Definition and Overview
Choose Stainless Steel Pressure Transducers
Top 5000 PSI Pressure Transducers: A Pre-Purchase Guide
Submersible Pressure Transducers 101: Guide to Precise Level Measurements
0-5 Volt Pressure Transducers
What Is Hydrostatic Pressure?
Sino-Inst offers kinds of DP transmitters, for differential pressure, level, and so on. A wide variety of DP transmitters are available to you.
You can also choose from the single flange, double flange, absolute pressure, low pressure,
high pressure to match your production conditions.
There are different styles of differential pressure transmitters.
Sino-Inst differential pressure transmitters products are exported,
and most popular in North America, Western Europe, India, Pakistan, and South America.
You can ensure product safety by selecting from certified material, including ISO9001… certification.
Request a Quote
DP transmitters for Sale-Differential Pressure Technology

DP transmitters are Differential Pressure Transmitters. DP transmitter measures the pressure difference between the gas or liquid at both ends of the transmitter. Output 4~20mA, 0~5V. Used for liquid level, density and pressure of liquid, gas and steam.
Product SKU: DP 3151
Product Brand: Sino-Inst
Product Currency: USD
Product Price: 200
Price Valid Until: 2099-09-09
Product In-Stock: PreOrder
5


